Skip to main content Contents Prev Up Next \(\require{cancel}\require{mhchem}\let\vecarrow\vec
\renewcommand{\vec}{\mathbf}
\newcommand{\ihat}{\vec{i}}
\newcommand{\jhat}{\vec{j}}
\newcommand{\khat}{\vec{k}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\proj}{proj}
\newcommand{\kg}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kg} }
\newcommand{\lbm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lbm} }
\newcommand{\slug}[1]{#1~\mathrm{slug}}
\newcommand{\m}[1]{#1~\mathrm{m}}
\newcommand{\km}[1]{#1~\mathrm{km}}
\newcommand{\cm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{cm}}
\newcommand{\mm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{mm}}
\newcommand{\ft}[1]{#1~\mathrm{ft}}
\newcommand{\yd}[1]{#1~\mathrm{yd}}
\newcommand{\inch}[1]{#1~\mathrm{in}}
\newcommand{\mi}[1]{#1~\mathrm{mi}}
\newcommand{\N}[1]{#1~\mathrm{N} }
\newcommand{\kN}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kN} }
\newcommand{\MN}[1]{#1~\mathrm{MN} }
\newcommand{\lb}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb} }
\newcommand{\lbf}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lbf} }
\newcommand{\Nm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{N}\!\cdot\!\mathrm{m} }
\newcommand{\kNm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kN}\!\cdot\!\mathrm{m} }
\newcommand{\ftlb}[1]{#1~\mathrm{ft}\!\cdot\!\mathrm{lb} }
\newcommand{\ftlbf}[1]{#1~\mathrm{ft}\!\cdot\!\mathrm{lbf} }
\newcommand{\inlb}[1]{#1~\mathrm{in}\!\cdot\!\mathrm{lb} }
\newcommand{\lbperft}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{ft} }
\newcommand{\lbperin}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{in} }
\newcommand{\Nperm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{N}/\mathrm{m} }
\newcommand{\kgperkm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kg}/\mathrm{km} }
\newcommand{\psinch}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{in}^2 }
\renewcommand{\psi}[1]{#1~\mathrm{psi} }
\newcommand{\pqinch}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{in}^3 }
\newcommand{\psf}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{ft}^2 }
\newcommand{\pqf}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{ft}^3 }
\newcommand{\Nsm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{N}/\mathrm{m}^2 }
\newcommand{\kgsm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kg}/\mathrm{m}^2 }
\newcommand{\kgqm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kg}/\mathrm{m}^3 }
\newcommand{\Pa}[1]{#1~\mathrm{Pa} }
\newcommand{\kPa}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kPa} }
\newcommand{\aSI}[1]{#1~\mathrm{m}/\mathrm{s}^2 }
\newcommand{\aUS}[1]{#1~\mathrm{ft}/\mathrm{s}^2 }
\newcommand{\mps}[1]{#1~\mathrm{m/s} }
\newcommand{\mph}[1]{#1~\mathrm{mi/hr} }
\newcommand{\unit}[1]{#1~\mathrm{unit} }
\newcommand{\ang}[1]{#1^\circ }
\newcommand{\second}[1]{#1~\mathrm{s} }
\newcommand{\minute}[1]{#1~\mathrm{min} }
\newcommand{\hr}[1]{#1~\mathrm{hr} }
\newcommand{\lt}{<}
\newcommand{\gt}{>}
\newcommand{\amp}{&}
\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}
\newcommand{\fillinmath}[1]{\mathchoice{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\displaystyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\textstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptscriptstyle\phantom{\,#1\,}$}}}
\)
Section 2.5 Torque
Torque is the rotational equivalent of force. It is the measure of the tendency of a force to rotate an object around an axis of rotation. In simple terms, torque is the turning force that causes an object to rotate, turn or twist.
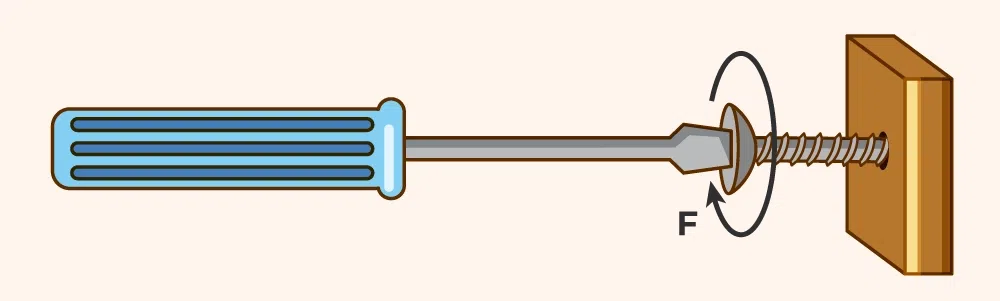
Figure 2.5.1. Example of Torque, Screwdriver turning a screw Different terms, including as moment or moment of force are interchangeably used to describe torque.
Torque is a vector quantity , which means that a torque has both magnitude and direction . These properties will be described in the next section.