Subsection 2.5.5 Torque and Gear Ratios
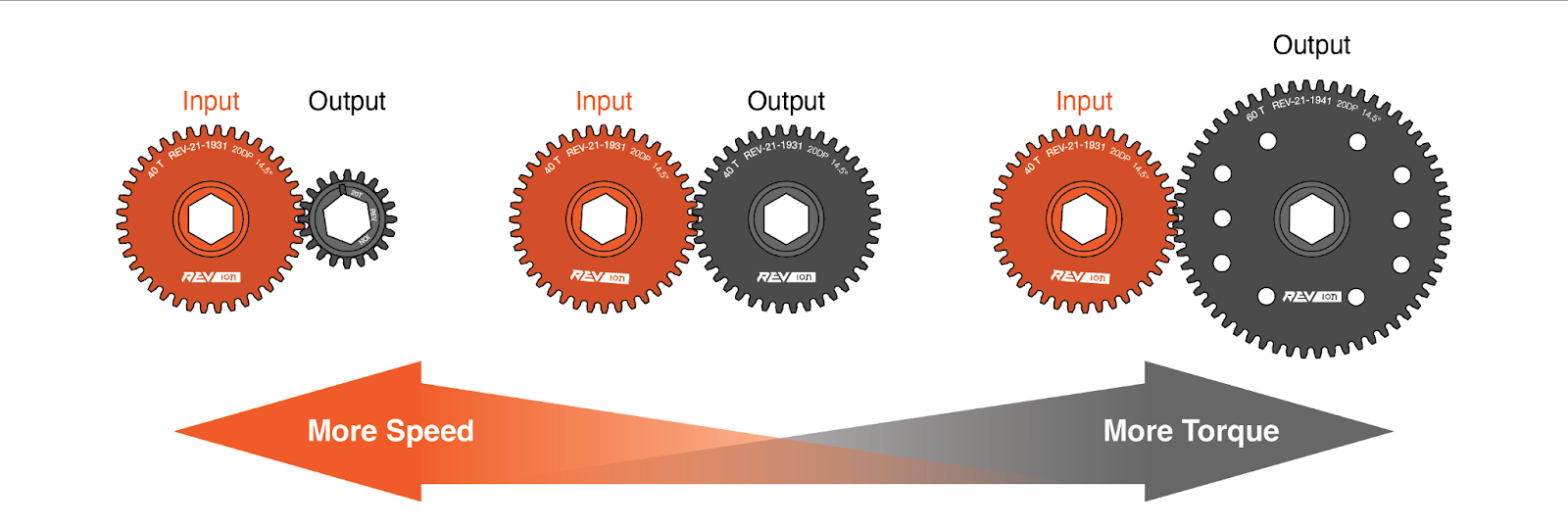
It is often necessary to increase or decrease the torque produced by a motor to suit different applications. Recall that the length of a lever can increase or decrease the force on an object at the expense of the distance through which the lever must be pushed. Similarly, the torque produced by a motor can be increased or decreased through the use of gearing. An increase in torque comes with a proportional decrease in rotational speed. The meshing of two gear teeth can be viewed as equivalent to the interaction of a pair of levers as shown in Figure 2.5.10.
When a larger gear drives a smaller one, for one rotation of the larger gear the small gear must complete more revolutions - so the output will be faster than the input. If the situation is reversed, and a smaller gear drives a larger output gear, then for one rotation of the input the output will complete less than one revolution – so the output will be slower than the input. The ratio of the sizes of the two gears is proportional to the speed and torque changes between them.