Skip to main content Contents Prev Up Next \(\require{cancel}\require{mhchem}\let\vecarrow\vec
\renewcommand{\vec}{\mathbf}
\newcommand{\ihat}{\vec{i}}
\newcommand{\jhat}{\vec{j}}
\newcommand{\khat}{\vec{k}}
\DeclareMathOperator{\proj}{proj}
\newcommand{\kg}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kg} }
\newcommand{\lbm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lbm} }
\newcommand{\slug}[1]{#1~\mathrm{slug}}
\newcommand{\m}[1]{#1~\mathrm{m}}
\newcommand{\km}[1]{#1~\mathrm{km}}
\newcommand{\cm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{cm}}
\newcommand{\mm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{mm}}
\newcommand{\ft}[1]{#1~\mathrm{ft}}
\newcommand{\yd}[1]{#1~\mathrm{yd}}
\newcommand{\inch}[1]{#1~\mathrm{in}}
\newcommand{\mi}[1]{#1~\mathrm{mi}}
\newcommand{\N}[1]{#1~\mathrm{N} }
\newcommand{\kN}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kN} }
\newcommand{\MN}[1]{#1~\mathrm{MN} }
\newcommand{\lb}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb} }
\newcommand{\lbf}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lbf} }
\newcommand{\Nm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{N}\!\cdot\!\mathrm{m} }
\newcommand{\kNm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kN}\!\cdot\!\mathrm{m} }
\newcommand{\ftlb}[1]{#1~\mathrm{ft}\!\cdot\!\mathrm{lb} }
\newcommand{\ftlbf}[1]{#1~\mathrm{ft}\!\cdot\!\mathrm{lbf} }
\newcommand{\inlb}[1]{#1~\mathrm{in}\!\cdot\!\mathrm{lb} }
\newcommand{\lbperft}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{ft} }
\newcommand{\lbperin}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{in} }
\newcommand{\Nperm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{N}/\mathrm{m} }
\newcommand{\kgperkm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kg}/\mathrm{km} }
\newcommand{\psinch}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{in}^2 }
\renewcommand{\psi}[1]{#1~\mathrm{psi} }
\newcommand{\pqinch}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{in}^3 }
\newcommand{\psf}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{ft}^2 }
\newcommand{\pqf}[1]{#1~\mathrm{lb}/\mathrm{ft}^3 }
\newcommand{\Nsm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{N}/\mathrm{m}^2 }
\newcommand{\kgsm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kg}/\mathrm{m}^2 }
\newcommand{\kgqm}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kg}/\mathrm{m}^3 }
\newcommand{\Pa}[1]{#1~\mathrm{Pa} }
\newcommand{\kPa}[1]{#1~\mathrm{kPa} }
\newcommand{\aSI}[1]{#1~\mathrm{m}/\mathrm{s}^2 }
\newcommand{\aUS}[1]{#1~\mathrm{ft}/\mathrm{s}^2 }
\newcommand{\mps}[1]{#1~\mathrm{m/s} }
\newcommand{\mph}[1]{#1~\mathrm{mi/hr} }
\newcommand{\unit}[1]{#1~\mathrm{unit} }
\newcommand{\ang}[1]{#1^\circ }
\newcommand{\second}[1]{#1~\mathrm{s} }
\newcommand{\minute}[1]{#1~\mathrm{min} }
\newcommand{\hr}[1]{#1~\mathrm{hr} }
\newcommand{\lt}{<}
\newcommand{\gt}{>}
\newcommand{\amp}{&}
\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}
\newcommand{\fillinmath}[1]{\mathchoice{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\displaystyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\textstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptscriptstyle\phantom{\,#1\,}$}}}
\)
Section 7.2 Basic Steam Cycle
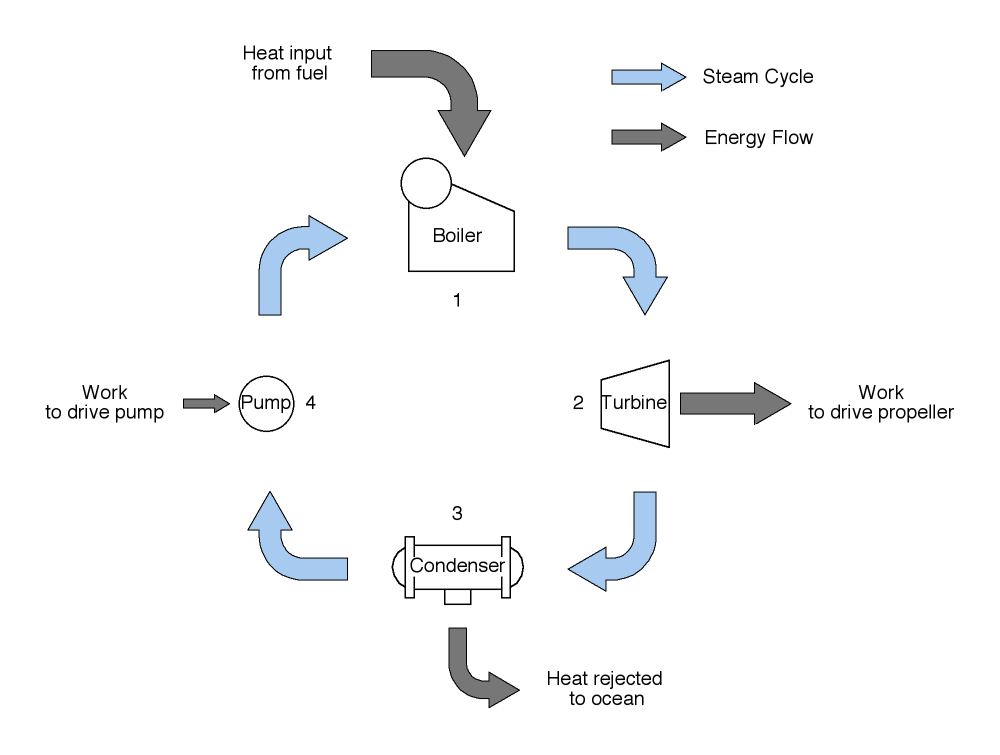
Figure 7.2.1 shows a very simplified version of the steam cycle, which is an appropriate starting point for our discussion of ship’s propulsion.
The steam cycle is an example of what is known by engineers as a cyclic heat engine . It is called cyclic , because it operates on a cycle. It uses a working fluid, water, which travels from point to point through the cycle, changing form and carrying energy, but eventually returning to the starting point restored to the same state that it started with. It is called a heat engine , because it transforms heat , which is a form of energy, into work , another form of energy. The thermodynamic name for this cycle is the Rankine Cycle .
Figure 7.2.1. Simplified Steam Cycle The four stages of the steam cycle will be described, and then the cycle will be described again, this times from the perspective of the Rankine Cycle.