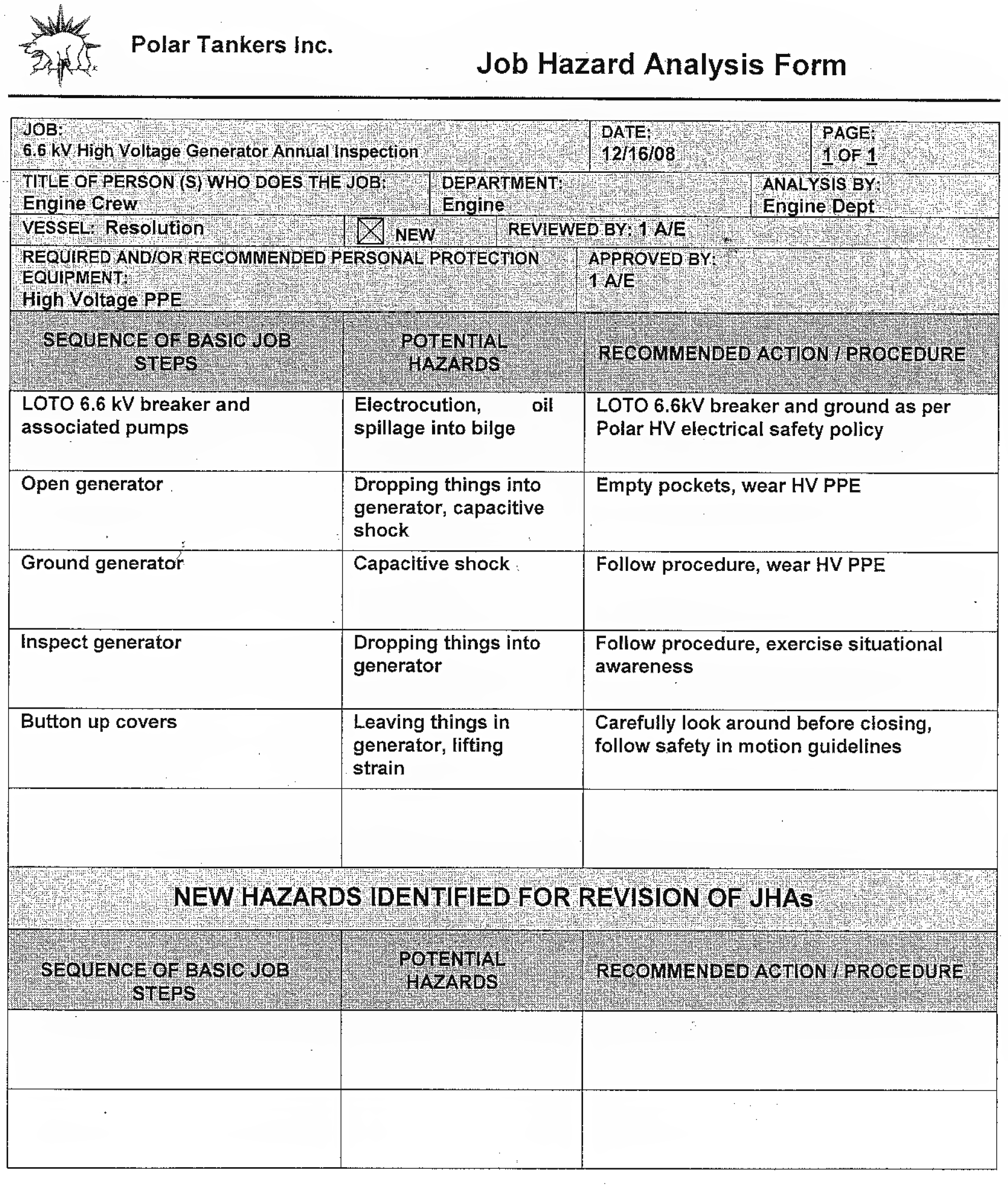
Subsection 1.2.2 Job Hazard Analysis
A job hazard analysis (JHA), also known as ajob safety analysis(JSA), is a systematic process used to identify and analyze potential hazards or risks associated with specific job tasks or activities. Its primary purpose is to reduce the risk of accidents by identifying potential hazards and developing appropriate controls to mitigate them.
The process typically involves breaking down a job into its individual steps and examining each step to identify potential hazards. Hazards can include physical hazards (e.g., machinery, equipment, or environmental conditions), chemical hazards (e.g., exposure to hazardous substances), biological hazards (e.g., exposure to infectious agents), ergonomic hazards (e.g., repetitive motion or lifting heavy objects), or any other factors that could pose a risk to worker safety and health.
The key steps in conducting a job hazard analysis typically include:
- Select the job or task to be analyzed.
- Break down the job into steps.
- Identify potential hazards for each step.
- Determine the risk level for each identified hazard. Risk level multiplies severity and the likelihood of each identified hazard.
- Develop hazard controls to eliminate or minimize the hazards. This might include engineering controls (e.g., machine guarding), administrative controls (e.g., training or procedures), or personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Communicate the findings to workers and stakeholders to ensure awareness and buy-in.
- Regularly review and update the job hazard analysis.
This results of the JHA can be shared with the crew during a toolbox talk in order to raise awareness about known hazards, reinforce safe work practices, and promote a culture of safety. These talks are usually conducted before the start of the work day.
Systematically analyzing and communicating job hazards and implementing appropriate controls helps to create a safer workplace.